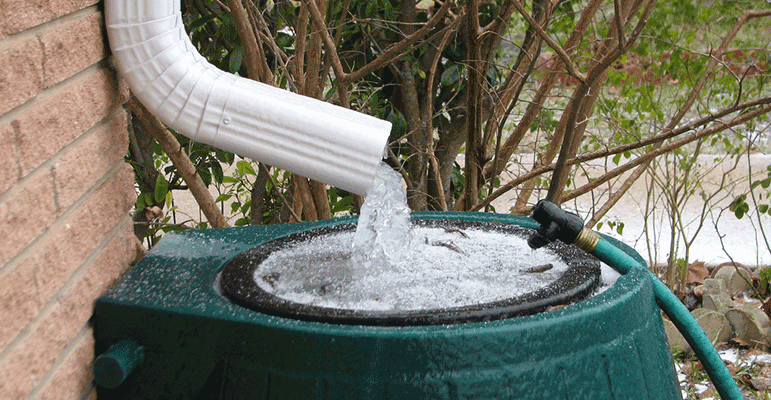

It simply means “Catch and store the rain water in the purest form for further use”. It is a simple technique of collecting rainwater that runs from catchment areas like roofs, pavements, roads, parks, open land etc. and storing it in storage tanks (for immediate use) or in the underground aquifers – natural or man-made for ground water recharge. Thus, rainwater can be stored in tanks and then used for many purposes later. Alternatively, it can be done to replenish the groundwater so that the dug wells/tube wells in the area keep on yielding water.
Rainwater may be charged into the groundwater aquifers through any suitable structures like dugwells, borewells, recharge trenches and recharge pits.Various recharge structures are possible - some which promote the percolation of water through soil strata at shallower depth (e.g., recharge trenches, permeable pavements) whereas others conduct water to greater depths from where it joins the groundwater (e.g. recharge wells). At many locations, existing structures like wells, pits and tanks can be modified as recharge structures, eliminating the need to construct any structures afresh.
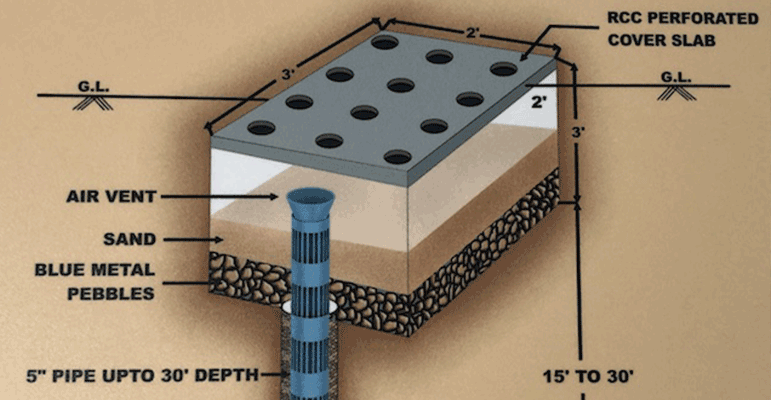
A recharge pit is 1.5m to 3m wide and 2m to 3m deep. The excavated pit is lined with a brick/stone wall with openings (weep-holes) at regular intervals. The top area of the pit can be covered with a perforated cover. Design procedure is the same as that of a settlement tank.
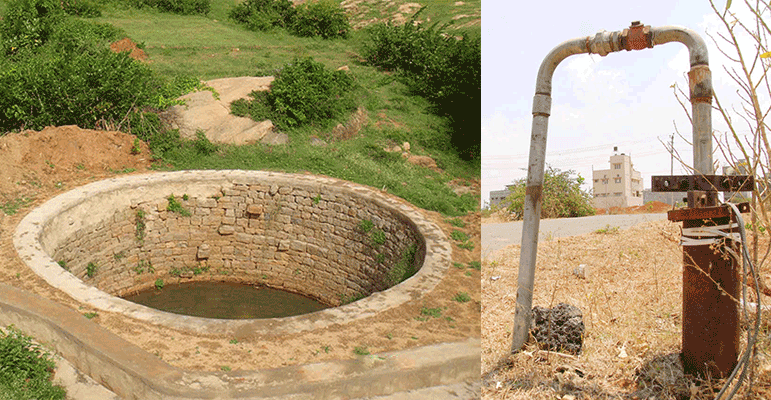
In alluvial and hard rock areas, there are thousands of wells which have either gone dry or whose water levels have declined considerably. These can be recharged directly with rooftop run-off. Rainwater that is collected on the rooftop of the building is diverted by drain pipes to a settlement or filtration tank, from which it flows into the recharge well (borewell or dugwell).
If a tubewell is used for recharging, then the casing (outer pipe) should preferably be a slotted or perforated pipe so that more surface area is available for the water to percolate. Developing a borewell would increase its recharging capacity (developing is the process where water or air is forced into the well under pressure to loosen the soil strata surrounding the bore to make it more permeable).
If a dugwell is used for recharge, the well lining should have openings (weep-holes) at regular intervals to allow seepage of water through the sides. Dugwells should be covered to prevent mosquito breeding and entry of leaves and debris. The bottom of recharge wells should be desilted annually to maintain the intake capacity.
Providing the following elements in the system can ensure the quality of water entering the recharge wells:
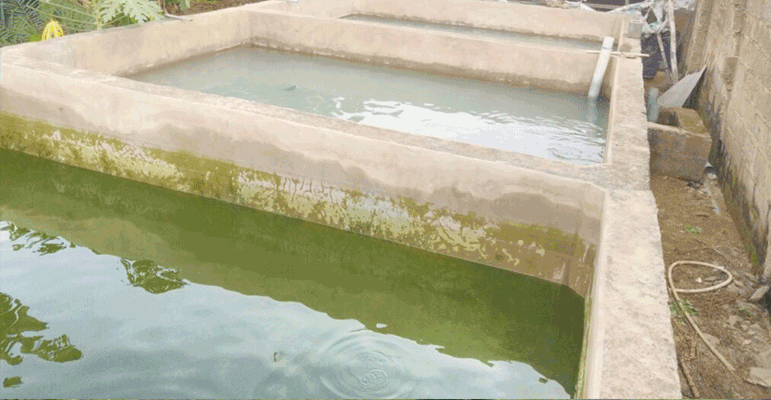

Settlement tanks are used to remove silt and other floating impurities from rainwater. A settlement tank is like an ordinary storage container having provisions for inflow (bringing water from the catchment), outflow (carrying water to the recharge well) and overflow. A settlement tank can have an unpaved bottom surface to allow standing water to percolate into the soil.
In case of excess rainfall, the rate of recharge, especially of borewells, may not match the rate of rainfall. In such situations, the desilting chamber holds the excess amount of water till it is soaked up by the recharge structure. Thus, the settlement chamber acts like a buffer in the system.
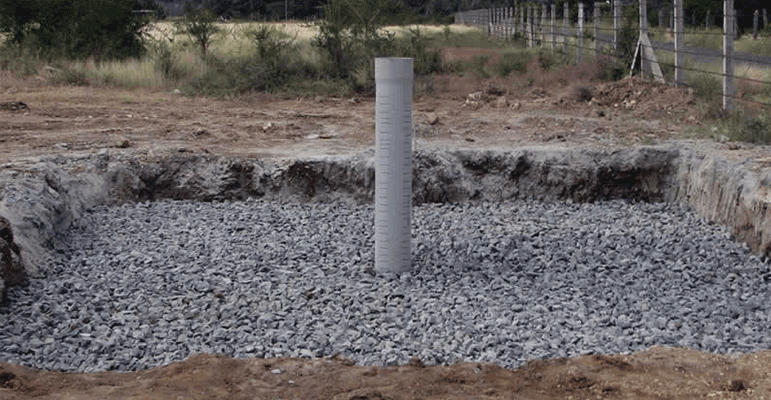

In this case the rooftop runoff is not directly led into the service tubewells, to avoid chances of contamination of groundwater. Instead rainwater is collected in a recharge well, which is a temporary storage tank (located near the service tubewell), with a borehole, which is shallower than the water table. This borehole has to be provided with a casing pipe to prevent the caving in of soil, if the strata is loose. A filter chamber comprising of sand, gravel and boulders is provided to arrest the impurities.
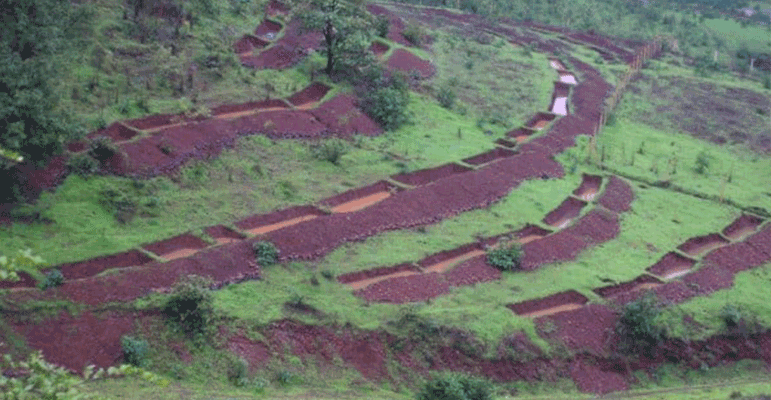

A recharge trench is a continuous trench excavated in the ground and refilled with porous media like pebbles, boulders or broken bricks. A recharge trench can be 0.5 m to 1 m wide and 1 m to 1.5 m deep. The length of the recharge trench is decided as per the amount of runoff expected. The recharge trench should be periodically cleaned of accumulated debris to maintain the intake capacity. In terms of recharge rates, recharge trenches are relatively less effective since the soil strata at depth of about 1.5 metres is generally less permeable. For recharging through recharge trenches, fewer precautions have to be taken to maintain the quality of the rainfall runoff. Runoff from both paved and unpaved catchments can be tapped.
If you are planning for a Rainwater Harvesting system for your home, society or any space. It's the best time to contact VS Company experts. We have a numerous amount of experience from convienceal to modular structure. We promise, you will not get disappointed while talking with us.